What is a Buck Converter? Understanding Its Function and Applications
The buck converter, a crucial component in the field of power electronics, has garnered the attention of engineers and industry specialists alike. According to Dr. Emily Zhang, a renowned expert in power management solutions, "The buck converter is essential for efficient voltage regulation, providing not only energy savings but also improving the overall performance of electronic devices." This statement encapsulates the significance of buck converters in modern applications, where reducing power loss is paramount.
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for efficient power supply solutions has led to increased utilization of buck converters in various industries, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics. These converters excel at stepping down voltage levels while maintaining high current efficiency, making them indispensable for battery-powered devices and renewable energy systems. Understanding the operational principles and applications of buck converters enables engineers to design more efficient systems that meet the growing energy needs of today's society.
In this article, we will delve into the functional mechanics of buck converters, exploring how they achieve voltage regulation and the myriad of applications they serve. By analyzing real-world examples and expert insights, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the importance of buck converters in driving energy efficiency and innovation across multiple sectors.

What is a Buck Converter?
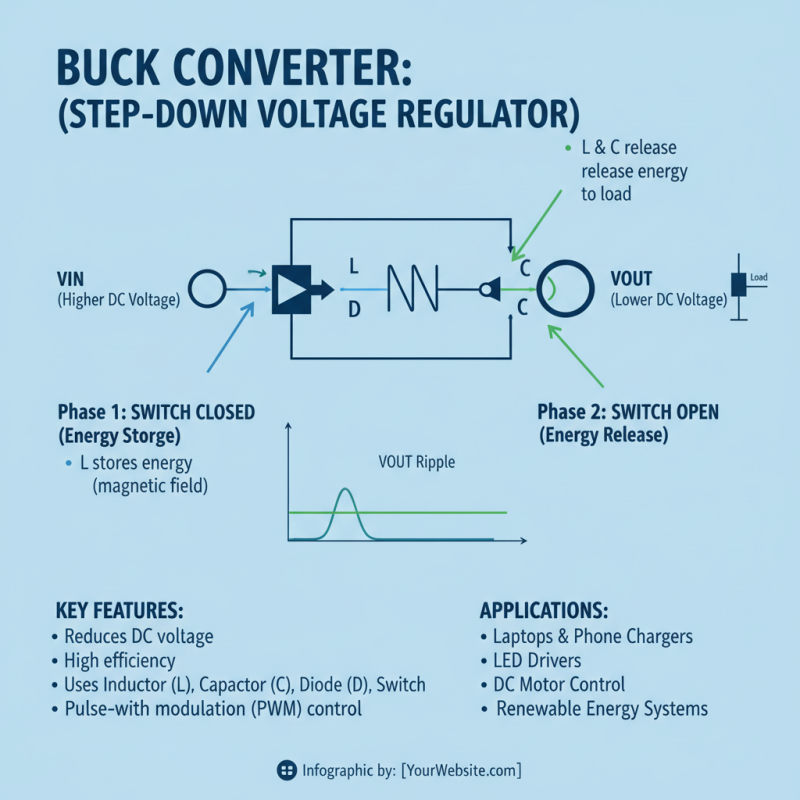
A buck converter, also known as a step-down converter, is an essential electrical component designed to reduce voltage from a higher level to a lower level while maintaining high efficiency. It operates using a combination of inductors, capacitors, and switches, typically managed by a control circuit. When the switch within a buck converter closes, the inductor stores energy; when the switch opens, the energy is released to the output, providing a steady lower voltage. This transformation facilitates numerous applications in various electronic devices, including power supplies in laptops, DC motor drives, and renewable energy systems.
The efficiency of a buck converter is one of its standout features, often exceeding 90%, making it a preferred choice in battery-operated applications where power conservation is crucial. Its compact size and capability to handle a wide range of input voltages make it versatile in consumer electronics and automotive systems. Furthermore, the simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into complex circuits, providing robust solutions for voltage regulation needs. Whether used in charging devices or as part of larger power management systems, the buck converter plays a pivotal role in modern electronics.
Basic Principles of Buck Converter Operation
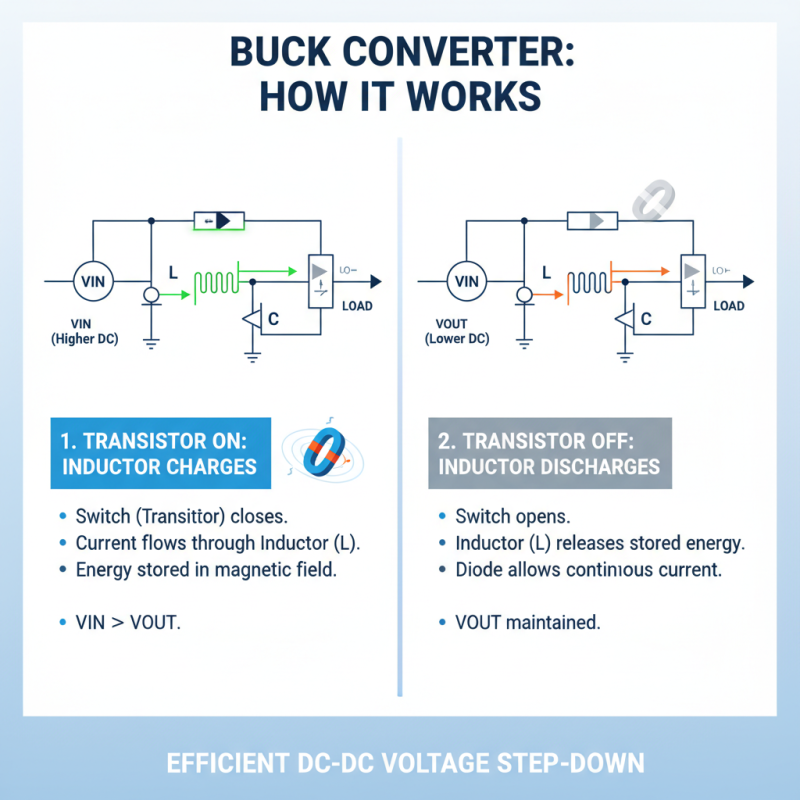
A buck converter is a type of DC-DC converter that efficiently steps down voltage from a higher level to a lower level while maintaining a specific level of output current. The basic operation hinges on a switching element, typically a transistor, and an inductor. When the transistor is turned on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. As the inductor charges, the input voltage is supplied to the output, allowing the converter to deliver power to the load. Once the transistor turns off, the inductor releases the stored energy to the output, resulting in a continuous flow of power.
The switching frequency and duty cycle are critical parameters that dictate the performance of a buck converter. The duty cycle, which is the ratio of the time the transistor is on to the total time of the switching cycle, determines the output voltage. A higher duty cycle results in a higher output voltage, whereas a lower duty cycle yields a lower output voltage. The use of feedback mechanisms helps maintain stable output voltage despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions. Additionally, the buck converter's efficiency, often exceeding 90%, makes it a preferred choice in applications such as power supplies for portable devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems, where conserving energy and maximizing battery life is essential.
Key Components of a Buck Converter Explained
A buck converter, also known as a step-down converter, is a crucial component in modern power management systems. It efficiently steps down voltage from a higher level to a lower level, which is essential for devices requiring lower voltage levels to operate. Understanding the key components of a buck converter is fundamental to grasping its function and applications. The primary components include an inductor, a diode, a switch (usually a transistor), and a capacitor.
The inductor plays a vital role in storing energy when the switch is closed and releasing it when the switch is open. This process creates a more stable output voltage, which is critical in applications ranging from consumer electronics to industrial automation. A recent report from the International Energy Agency noted that implementing buck converters can enhance energy efficiency in power supply systems, reducing energy losses by up to 95%. Meanwhile, capacitors smooth the output voltage, ensuring that the current delivered to the load is stable, which is particularly important for sensitive electronics.
Tips: When designing a buck converter circuit, it's crucial to select components with suitable ratings for your specific application. Overrating components can lead to unnecessary costs, while underestimating them can cause failures. Always consider the inductor's saturation current and the switching frequency, as these can significantly impact the converter's performance. Additionally, evaluating thermal management solutions will ensure reliability in demanding environments.
Buck Converter Efficiency Comparison
This chart displays the efficiency of buck converters at various output voltages. As seen from the data, the efficiencies generally vary between 88% to 92%, indicating the performance variations based on the desired output voltage.
Applications of Buck Converters in Modern Electronics
Buck converters play a crucial role in modern electronics, primarily by converting a higher voltage to a lower voltage efficiently. This capability is essential in various applications where power management is vital. For instance, smartphones and laptops utilize buck converters to optimize battery life. By stepping down voltage while maintaining high efficiency, these devices can prolong usage time without compromising performance. The compact size and lightweight nature of buck converters also make them ideal for portable electronics.
Another significant application of buck converters is in renewable energy systems. In solar power setups, buck converters help manage the voltage from solar panels to ensure that batteries are charged effectively without loss of power. Additionally, in electric vehicles, these converters efficiently regulate the voltage supplied to various components, including motors and control units. The adaptability and efficiency of buck converters make them indispensable in smart grids, electric bikes, and even in powering LED lighting systems, where optimal energy usage is paramount.
What is a Buck Converter? Understanding Its Function and Applications - Applications of Buck Converters in Modern Electronics
| Application | Description | Example Devices | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides efficient voltage step-down for various electronic devices. | Laptops, smartphones, and tablets | High efficiency, reduced heat generation |
| Electric Vehicles | Converts battery voltage to lower voltages for vehicle components. | Battery management systems, motor controllers | Improved range, power optimization |
| LED Drivers | Regulates voltage and current supplied to LEDs for consistent brightness. | LED lighting systems | Energy efficiency, longer LED life |
| Consumer Electronics | Used in various consumer devices to convert voltages. | Game consoles, home appliances | Compact design, flexibility in application |
| Telecommunications | Supplies power to networking equipment with various voltage levels. | Routers, switches | Stable operation, high reliability |
Advantages and Limitations of Using Buck Converters
Buck converters are widely used in various applications due to their efficient step-down voltage regulation. One significant advantage of using buck converters is their high efficiency, often exceeding 90%. This efficiency is especially beneficial in battery-powered devices where maximizing battery life is crucial. By minimizing energy loss, buck converters enable longer operation times and reduced heat generation, which can lead to more compact designs. Additionally, their ability to provide a stable output voltage while handling wide input voltage ranges makes them versatile components in power management circuits.
However, there are limitations associated with buck converters. One of the main challenges is their complexity; they require careful design considerations, including the selection of appropriate inductors and capacitors. This complexity can lead to increased manufacturing costs and a steeper learning curve for engineers. Furthermore, buck converters can produce voltage ripple and electromagnetic interference, which may necessitate additional filtering solutions, complicating the overall circuit design. While these factors may limit their use in some applications, buck converters remain a preferred choice for efficient power conversion in many electronic devices.
Related Posts
-
How to Select the Best Buck Converter for Efficient Power Management in Your Application
-

10 Digital Best Practices for Enhancing Your Buck Converter Efficiency
-

Exploring the Future of Buck Converters at China's 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Insights and Innovations
-

Exploring DC DC Converter Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

How to Select the Right AC to DC Converter for Your Specific Needs
-
Unlocking Efficiency: How Buck Converters Achieve Over 95% Power Conversion in Modern Electronics
At Premium PSU, we are specialists in designing and manufacturing power conversion systems for the industrial market. Our product range includes high reliability power supplies from 50W to 72kW.
PREMIUM PSU
C/ Dolors Aleu, 19-21, 2nd Floor
08908 – Hospitalet de Llobregat
Barcelona-SPAIN
t.+34 93 223 26 85


