How to Choose the Right DC Converter for Your Project Needs
When embarking on an electronics project, selecting the right components is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Among these components, the DC converter plays a pivotal role. A DC converter is essential for managing voltage levels, enabling devices to function correctly and safely. Whether you are powering small electronic devices or complex systems, understanding how to choose the appropriate DC converter customized to your project's requirements can significantly influence your design's success.
The landscape of DC converters is vast, with various types available to suit differing applications. Factors such as input and output voltage specifications, efficiency ratings, and load requirements must be carefully considered. Moreover, the converter's footprint and thermal management capabilities are equally important, particularly in compact designs where space is at a premium. By gaining insight into these essential aspects, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions during the selection process, ultimately leading to a more reliable and effective end product.
In this guide, we will explore the critical factors to consider when choosing a DC converter for your project needs. From understanding the different types available to recognizing the key specifications that align with your requirements, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview that will aid you in making the best choice for your specific application.
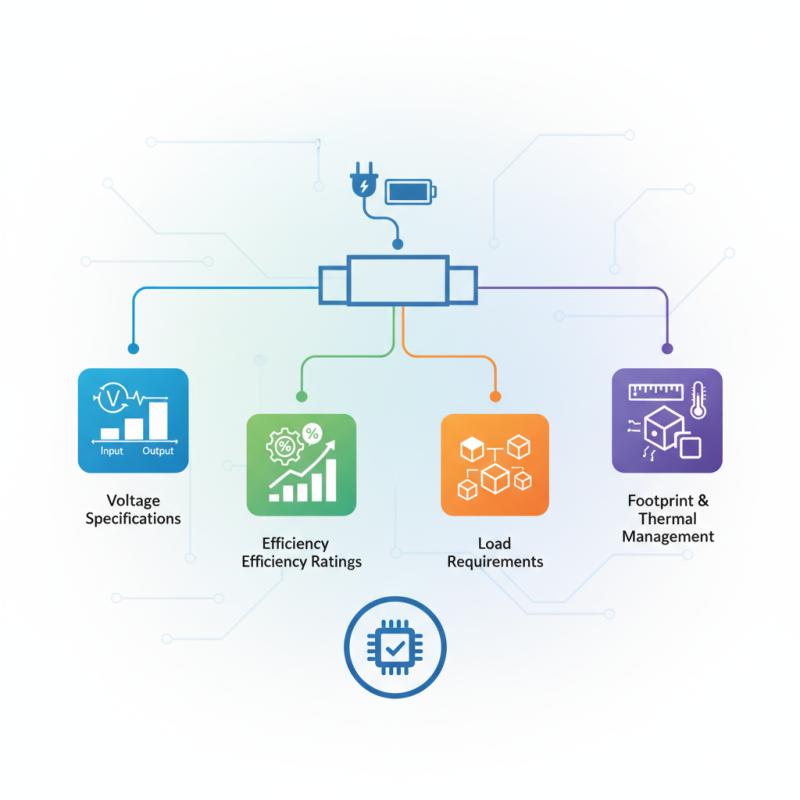
Understanding the Basics of DC Converters and Their Functions
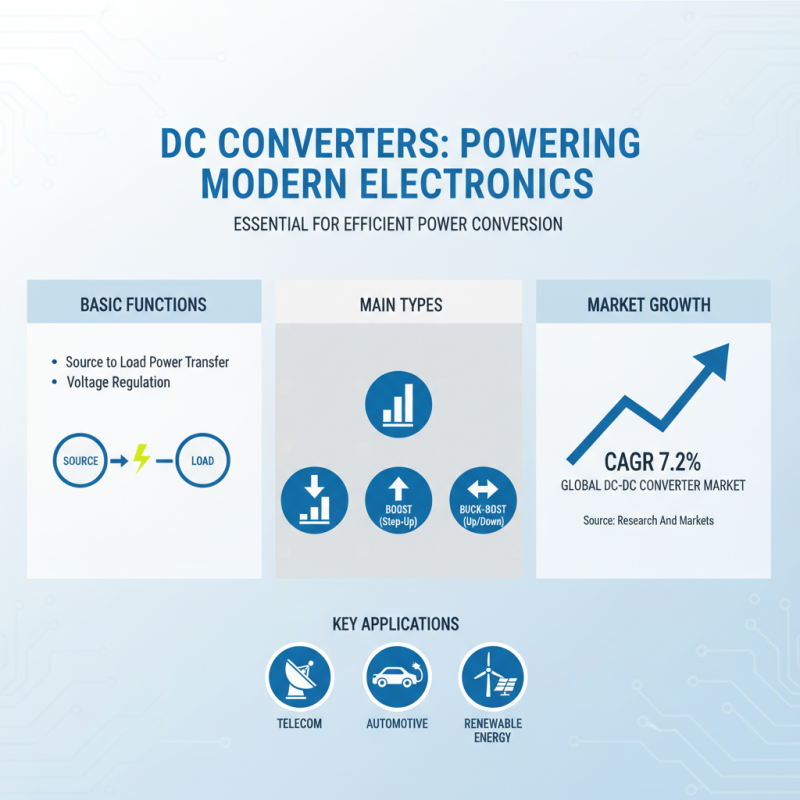
DC converters play a critical role in a variety of electronic applications, ensuring efficient power conversion from a source to a load. Understanding their basic functions starts with recognizing the main types of converters available, such as buck converters (step-down), boost converters (step-up), and buck-boost converters that can both increase and decrease voltage. According to a report by Research And Markets, the global DC-DC converter market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.2%, highlighting the increasing demand across sectors like telecommunications, automotive, and renewable energy.
The primary function of a DC converter is to alter the voltage level while maintaining power balance. For instance, a buck converter steps down an input voltage to produce a lower output voltage, ideal for portable devices that require lower power consumption. In contrast, boost converters elevate voltage levels for applications such as LED drivers. Moreover, efficiency ratings are paramount; modern converters can achieve efficiencies exceeding 90%. This efficiency not only maximizes the energy transferred to the load but also minimizes heat generation, contributing to the longevity of the devices involved. Understanding these fundamentals enables project managers and engineers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific project needs.
Identifying Your Project's Power Requirements and Specifications
When selecting the appropriate DC converter for your project, understanding the power requirements and specifications is crucial. Start by determining the voltage and current demands of your device; for optimal performance, ensure the output voltage matches the operational voltage needed by your components. According to a recent industry report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, nearly 45% of project failures are attributed to mismatched voltage requirements. This highlights the importance of careful assessment at the outset.
In addition to voltage, it’s essential to account for the total current draw of your project. Utilize a multimeter to measure the actual current needed during operation, which may differ from theoretical calculations due to inefficiencies or additional power draw from peripherals. As a tip, always consider a margin of safety by selecting a converter that can deliver slightly more current than you anticipate needing, typically around 20% more. This not only ensures reliability but also accommodates future expansions or unexpected power increases.
Additionally, consider factors such as efficiency ratings and thermal management. According to the Energy Efficiency Directive, converters with efficiency ratings above 90% not only reduce energy consumption but also minimize heat generation, which is vital for maintaining system longevity. Implementing effective thermal management strategies, such as heat sinks or active cooling, can further enhance performance and reliability. Thus, a thorough analysis of these specifications can lead to an informed choice of a DC converter tailored to your project needs.
DC Converter Power Requirements
This chart illustrates the power requirements for various DC voltage levels commonly used in projects. Each voltage level has specific wattage needs, which are critical in selecting the right DC converter for efficient performance.
Evaluating Different Types of DC Converters Available in the Market
When selecting a DC converter for your project, it's essential to evaluate the various types available in the market to ensure you choose the right one for your specific needs. The main types of DC converters include buck converters, boost converters, buck-boost converters, and linear regulators. Each of these has distinct operational principles and applications, which can significantly impact the performance of your project. For example, buck converters are efficient for stepping down voltage, making them ideal for battery-powered devices, whereas boost converters are beneficial for stepping up voltage from a lower level to a higher required level.
Tips: When assessing your options, consider the voltage and current specifications required by your application. Make sure to account for efficiency ratings as this will affect your heat management and overall energy consumption. Additionally, size and weight can be crucial in projects where space is limited, so be sure to look at the physical dimensions of the DC converter as well.
Another vital aspect to consider is the converter's control method—whether it's a fixed or adjustable output. Fixed output converters are simpler and often more reliable, while adjustable output converters offer flexibility in applications where the load may change. Assessing these features according to your project’s demands can lead to a more effective and reliable power solution.
Key Features to Look for in a DC Converter for Your Application
When selecting a DC converter for your project, it’s essential to focus on key features that align with your specific application. One of the foremost aspects to consider is the output voltage range. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ensuring that the converter can provide stable output within your required voltage limits is crucial for the overall reliability of your system. Options that offer adjustable output voltages can offer greater flexibility, which is especially important in applications where requirements may change over time.
Another critical feature to evaluate is the efficiency of the DC converter. High-efficiency converters generally operate above 85%, which minimizes heat generation and reduces energy costs. The Department of Energy (DOE) reports that improving system efficiency not only lowers operational expenses but also extends the lifespan of electronic components. Additionally, look for converters with built-in protections against over-voltage, under-voltage, and short circuits; these safety measures are vital in preventing damage to both the converter and other system components during unexpected conditions.
Lastly, consider the size and thermal management features of the DC converter. As devices become smaller and more compact, the demand for high-density packages grows. The industry trend indicates a shift toward modular designs that can dissipate heat more effectively. According to a recent report from the Power Sources Manufacturers Association (PSMA), advances in materials and cooling technologies are leading to more efficient thermal management solutions, which are essential for maintaining performance in high-power applications. Hence, selecting a converter that integrates these innovations can provide added durability and efficiency in your project.
Tips for Selecting a Reliable Vendor for DC Converters
When selecting a reliable vendor for DC converters, one should start by assessing the vendor's reputation and experience in the industry. A vendor with a strong track record typically provides assurance of quality and reliability. Look for companies that specialize in power conversion technology and have years of experience. Reading customer reviews and seeking recommendations can help gauge their reliability and service quality. Additionally, consider vendors that offer robust technical support and design assistance, which can be invaluable during the design and implementation phases of your project.
Another essential factor is the vendor's commitment to quality control and compliance with industry standards. Check if they have certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates that they adhere to rigorous quality management practices. It's also beneficial to inquire about their testing procedures and the reliability of their products under various operating conditions. A vendor that prioritizes quality assurance processes is more likely to provide converters that meet your project's specifications and reduce the likelihood of failures in the field. Overall, a thorough evaluation of vendor capabilities will lead to a more successful project outcome.
Related Posts
-

10 Digital Best Practices for Enhancing Your Buck Converter Efficiency
-
How to Select the Best Buck Converter for Efficient Power Management in Your Application
-

Exploring the Future of Buck Converters at China's 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Insights and Innovations
-
Unlocking Efficiency: How Buck Converters Achieve Over 95% Power Conversion in Modern Electronics
-

Understanding Buck Converters: The Key to Efficient Power Supply in Modern Electronics
-
What is a Buck Converter? Understanding Its Function and Applications
At Premium PSU, we are specialists in designing and manufacturing power conversion systems for the industrial market. Our product range includes high reliability power supplies from 50W to 72kW.
PREMIUM PSU
C/ Dolors Aleu, 19-21, 2nd Floor
08908 – Hospitalet de Llobregat
Barcelona-SPAIN
t.+34 93 223 26 85


