What is UPS Electrical and How Does it Work for Your Power Needs
In today's world, where technology plays an integral role in our daily lives, ensuring a reliable power supply is more crucial than ever. This is where UPS electrical systems come into play, providing critical backup power to keep essential devices running smoothly during outages or fluctuations in the electrical grid. A UPS, or Uninterruptible Power Supply, not only acts as a safety net for sensitive electronics but also helps in maintaining the workflow of businesses and organizations where downtime can lead to significant losses.
Understanding how UPS electrical systems operate can empower individuals and companies alike to make informed choices about their power management needs. From home offices to large data centers, these systems serve as guardians of equipment, preventing data loss and potential damage from abrupt power disruptions. This article delves into the fundamental aspects of UPS electrical technology, explaining its components and functionality, as well as providing insight into how it can be effectively integrated into various power requirements. As we explore the landscape of UPS electrical solutions, we aim to highlight the importance of robust, reliable power systems in an increasingly digital and interconnected environment.

What is UPS Electrical?
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems are critical for maintaining power continuity and safeguarding electronic devices from unexpected outages. A UPS is essentially a battery backup system that provides emergency power when the main supply fails. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global UPS market is expected to grow from $8.7 billion in 2020 to $13.8 billion by 2025, reflecting a robust demand for reliable power solutions across various industries including IT, healthcare, and telecommunications.
A UPS functions by continuously monitoring the power voltage and frequency. When it detects a drop in power supply or a total blackout, it instantly switches to its internal battery, ensuring that connected devices remain operational without interruption. This mechanism not only helps in avoiding data loss but also protects sensitive equipment from power surges that can cause significant damage. The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) highlights that about 80% of power outages are short-lived, lasting less than five minutes. However, even brief interruptions can wreak havoc on critical systems, making UPS systems essential for preserving data integrity and operational continuity.
Moreover, UPS systems can come with various features such as surge protection, voltage regulation, and even built-in energy management tools. This adaptability enhances their value in modern power infrastructure, as businesses increasingly rely on uninterrupted power for their digital operations. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that as global energy demand continues to rise, so does the need for efficient power management solutions, and UPS systems play a pivotal role in mitigating downtime while helping organizations achieve greater energy efficiency.
The Components of a UPS System
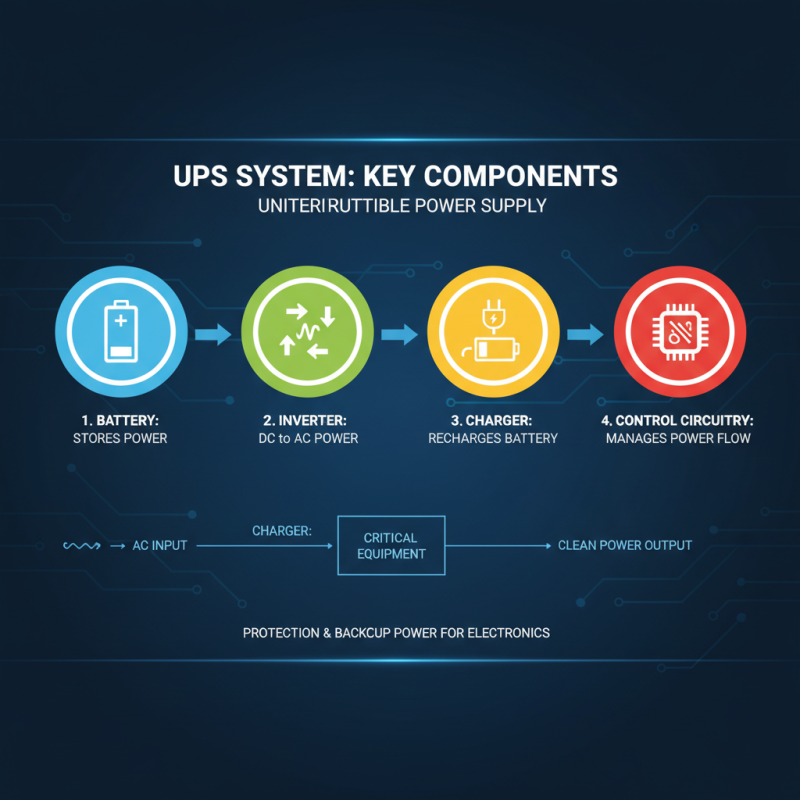
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system is crucial for providing backup power and protecting sensitive electronic equipment from interruptions. Understanding its key components is essential for optimizing its performance to meet your power needs. A standard UPS typically consists of a battery, inverter, charger, and control circuitry.
The battery stores energy, allowing the UPS to provide power instantly during an outage. The inverter converts the stored DC power into AC power, which is suitable for your devices. The charger ensures the battery remains charged while the UPS is running under normal conditions. Control circuitry monitors the system’s performance, managing power distribution and ensuring everything operates smoothly.
Tips for selecting a UPS system include evaluating your power requirements by calculating the total wattage of the devices that will be connected. Consider opting for a UPS with an extended battery runtime, especially if your work relies on critical applications. Regular maintenance is also vital. Periodically check battery health and replace it as necessary to ensure reliability during an outage. This proactive approach can help minimize downtime and protect your equipment from damage.
How a UPS Works: The Technology Behind It
A Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a critical component for ensuring that sensitive electronic devices and systems receive a stable power supply. It serves as a bridge between the main power source and the load, providing immediate backup power during outages or fluctuations. The technology behind a UPS is based on several key components, including batteries, an inverter, and a charger. According to industry reports, the global UPS market is projected to grow significantly, reaching approximately $10 billion by 2026, reflecting the increasing demand for reliable power solutions in various sectors such as IT, healthcare, and telecommunications.
The operation of a UPS revolves around its ability to detect power discrepancies. When an outage occurs, the UPS instantly switches to battery power, enabling a seamless transition to protect devices from data loss and hardware damage. The inverter then converts the stored DC (direct current) energy from the batteries into AC (alternating current) power, which is used by most electronic devices. A study by the TechNavio Research Group indicates that innovative technologies such as online double conversion and line-interactive designs enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of UPS systems, making them indispensable in environments where power reliability is paramount. By incorporating these advanced technologies, UPS systems not only provide backup power but also improve the overall power quality, extending the lifespan of connected equipment.
What is UPS Electrical and How Does it Work for Your Power Needs
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | The voltage supplied to the UPS. | 120V / 230V |
| Output Voltage | The voltage output from the UPS to the connected devices. | 120V / 230V |
| Battery Type | Type of battery used in UPS systems. | Lead-acid / Lithium-ion |
| Capacity | The power load the UPS can support. | 500VA - 3000VA |
| Transfer Time | Time taken to switch to battery power from mains. | 2ms - 10ms |
| Runtime | Duration the UPS can provide power during an outage. | 5 min - 1 hour |
Types of UPS Systems and Their Applications
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems are essential for a wide range of applications, providing backup power during outages and surge protection. The primary types of UPS systems include Offline/Standby, Line-Interactive, and Online (Double Conversion) systems. Each type caters to different power needs and offers varying levels of protection. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global UPS market is expected to grow from $9.9 billion in 2021 to $14.4 billion by 2026, underscoring the increasing reliance on these systems.
Offline/Standby UPS systems are the most basic and cost-effective solution, ideal for personal computers and small networks. They switch to battery power when a power failure is detected, offering surge protection and battery backup but only minimal conditioning of the power supply.
Line-Interactive UPS systems, which accounted for nearly 40% of the UPS market share in 2021, are designed for environments with fluctuating voltage. They provide automatic voltage regulation, making them suitable for small server rooms and networking equipment. On the other hand, Online UPS systems deliver the highest level of protection by continuously converting incoming AC power to DC and then back to AC. They are essential for critical applications in data centers and healthcare facilities, where any downtime can result in significant financial loss or jeopardize patient safety.
Each UPS type serves distinct purposes based on power quality requirements and budget constraints, making it vital for businesses to assess their specific needs when selecting a UPS solution. According to a report by Grand View Research, the demand for UPS systems is significantly driven by the increasing need for data protection and the growing deployment of data centers across various industries.
Benefits of Using a UPS for Power Needs
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is essential for ensuring the continuous operation of electrical equipment during power interruptions. One of the primary benefits of using a UPS is the protection it offers against data loss and equipment damage. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, 60% of businesses experience a significant data loss during a power outage, highlighting the critical need for reliable backup power systems. A UPS not only provides instantaneous power to connected devices but also conditions the voltage, helping to protect sensitive electronics from surges and sags.
Furthermore, implementing a UPS system can significantly improve operational efficiency. Research from the Electric Power Research Institute indicates that interruptions in power supply can cost businesses up to $150 billion annually in lost productivity. By integrating a UPS, organizations can mitigate downtime and maintain consistent power supply, leading to improved business continuity. Additionally, modern UPS systems often come with energy-efficient features and monitoring capabilities that enable businesses to optimize their power usage, contributing to overall cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 UPS Electrical Systems to Enhance Power Reliability and Efficiency
-

5 Essential Tips to Optimize Your UPS Electrical Systems for Maximum Efficiency
-
How to Choose the Right UPS Power System for Your Needs
-
Why You Need UPS Electrical Systems for Home and Business Protection
-

Ultimate Guide to Selecting the Best UPS Power Supply for Your Business
-

Discover the Advantages of Implementing UPS Power Solutions for Your Business
At Premium PSU, we are specialists in designing and manufacturing power conversion systems for the industrial market. Our product range includes high reliability power supplies from 50W to 72kW.
PREMIUM PSU
C/ Dolors Aleu, 19-21, 2nd Floor
08908 – Hospitalet de Llobregat
Barcelona-SPAIN
t.+34 93 223 26 85


